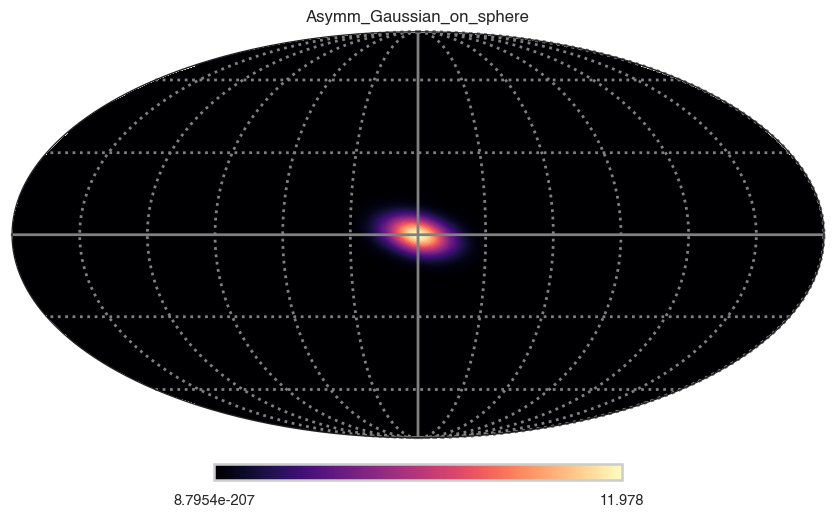
Asymm Gaussian on sphere
[3]:
# Parameters
func_name = "Asymm_Gaussian_on_sphere"
Description
[5]:
func.display()
- description: A bidimensional Gaussian function on a sphere (in spherical coordinates) see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaussian_function#Two-dimensional_Gaussian_function
- formula: $n.a.$
- parameters:
- lon0:
- value: 0.0
- desc: Longitude of the center of the source
- min_value: 0.0
- max_value: 360.0
- unit:
- is_normalization: False
- delta: 0.1
- free: True
- lat0:
- value: 0.0
- desc: Latitude of the center of the source
- min_value: -90.0
- max_value: 90.0
- unit:
- is_normalization: False
- delta: 0.1
- free: True
- a:
- value: 10.0
- desc: Standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution (major axis)
- min_value: 0.0
- max_value: 20.0
- unit:
- is_normalization: False
- delta: 1.0
- free: True
- e:
- value: 0.9
- desc: Excentricity of Gaussian ellipse
- min_value: 0.0
- max_value: 1.0
- unit:
- is_normalization: False
- delta: 0.09000000000000001
- free: True
- theta:
- value: 10.0
- desc: inclination of major axis to a line of constant latitude
- min_value: -90.0
- max_value: 90.0
- unit:
- is_normalization: False
- delta: 1.0
- free: True
- lon0:
Shape
The shape of the function on the sky.
[6]:
m=func(ra, dec)
hp.mollview(m, title=func_name, cmap="magma")
hp.graticule(color="grey", lw=2)